BOARD
News
|
[논문게재] High-temperature stability in Ti-based MAX phases: vacancy effects on mechanical properties 관리자 │ 2025-10-20 HIT 5858 |
|---|
|
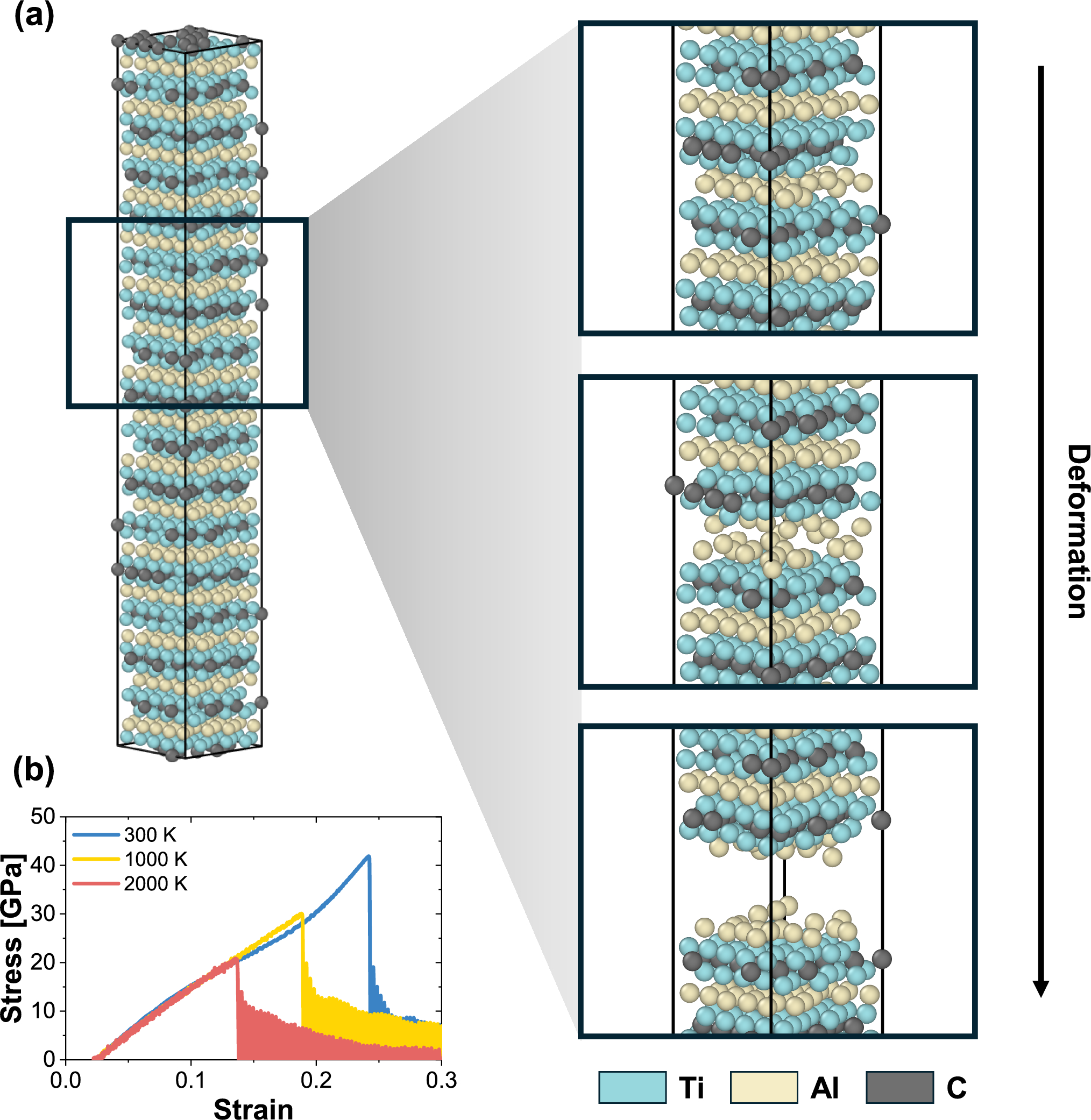
Title: High-temperature stability in Ti-based MAX phases: vacancy effects on mechanical properties Journal: Journal of Korean Ceramic Society Year: 2025 Impact factor: 3.8 Abstract: Tin+1AlCn MAX phases are of interest due to their high-temperature mechanical properties. In this study, we investigated their structural and mechanical properties up to 2000 K using molecular dynamics (MD) tensile simulations and density functional theory (DFT) calculations, focusing on the effect of vacancies. The presence of up to 12.5% Al vacancies reduced the vertical Young’s modulus by only 12.59% and left the UTS almost unchanged, demonstrating considerable mechanical robustness. In contrast, the same concentration of Ti vacancies degraded the Young’s modulus by 40.7% at 2000 K. Electron localization function (ELF) analysis confirmed that the mechanical properties are dominated by strong Ti–C covalent bonds, which are not weakened by Al vacancies. In comparison to B1-type TiC, whose Young’s modulus decreases by ~ 32% at 2000 K, Tin+1AlCn retains over 88% of its room-temperature vertical Young’s modulus. This work provides a theoretical basis for considering Tin+1AlCn MAX phases as potential high-temperature structural materials.
|
| 이전글 | [취업소식] 이진용 석사 LG에너지솔루션 합격 |
|---|---|
| 다음글 | [수상소식] 2025년도 한국세라믹학회 추계학술대회 KCerS 우수... |